Which Lymphoid Organ Filters Lymph?
All MCAT Biology Resources
Which of the following is Not a role of the lymphatic arrangement?
Possible Answers:
Thymus and spleen
Os marrow
Liver
Adenoids and tonsils
Caption:
All of the following are parts of the lymphatic organisation, except the liver. The liver is considered to exist primarily a part of the digestive system.
Which of the post-obit are you lot near likely to discover in the medulla of a lymph node?
Possible Answers:
B-cells
T-cells
Stromal cells
Dendritic cells
Explanation:
In the lymph node, the B-cells are located in the cortex and the T-cells are located in the medulla. The stromal cells are structural cells that are not particular to an area of the lymph node. Dendritic cells will move through the lymph node to present antigens to the adaptive allowed system cells.
Which of the following is a primary lymphoid structure?
I. Thymus
II. Spleen
3. Lymph node
Possible Answers:
Ii and III
I, 2, and 3
I just
Iii simply
Explanation:
Primary lymphoid tissues refer to the tissues where lymphoid cells are generated, while secondary lymphoid tissues are the functional organs of the lymphatic arrangement.
Lymphocytes are generated and adult in the os marrow and thymus only. The spleen and lymph nodes are examples of secondary lymphatic organs.
Hypersensitivity reactions occur when body tissues are affected past an abnormal allowed reaction. The consequence is damage to normal tissues and clinical illness. A peanut allergy is an example of a hypersensitivity reaction, but there are 3 boosted broad classes.
One class involves the abnormal production or deposition of antibodies. Antibodies are B-jail cell derived molecules that normally attach to pathogens, rendering them unable to keep an infection. When antibodies are produced confronting normal tissues, even so, disease tin result. Effigy 1 depicts a schematic structure of an antibody.
Antibodies can be divided into two peptide chains: heavy and lite. Heavy chains form the courage of the antibiotic, and are attached to light chains via covalent bonding. Each heavy and low-cal concatenation is then further divided into abiding and variable regions. Variable regions exhibit molecular diverseness, generating a unique chemic identity for each antibody. These unique patterns help guarantee that the body can produce antibodies to recognize many possible molecular patterns on invading pathogens.
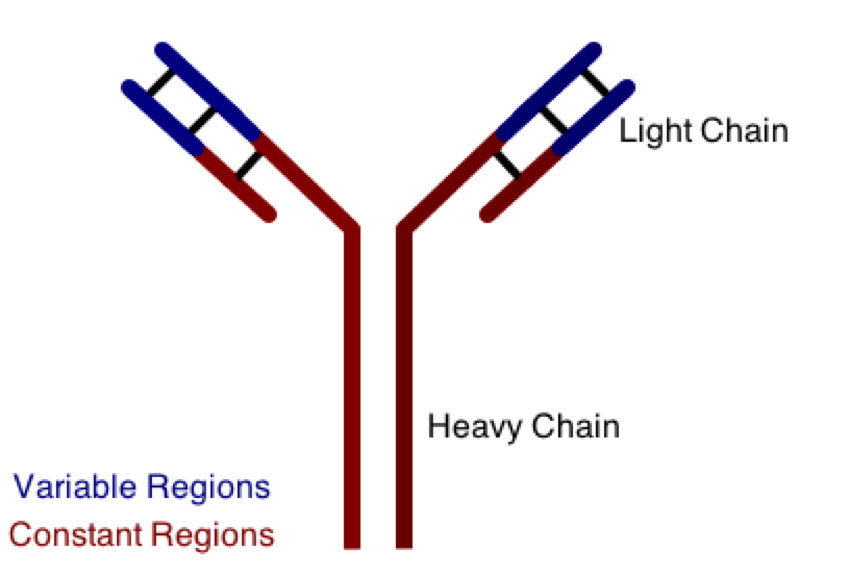
Antibodies and antigens interact in secondary lymphoid tissue, such as the spleen. In add-on to its role in promoting this interaction, what is the main function of the spleen?
Possible Answers:
Synthesize new white blood cells
Secrete digestive enzymes
Synthesize most serum proteins
Secrete systemic hormones
Filter senescent cerise blood cells
Correct answer:
Filter senescent red blood cells
Explanation:
The spleen has 2 main functions. The first main office is immunological, while its second function is to filter unhealthy (senescent) red blood cells.
Most digestive enzymes are secreted past the pancreas into the small intestine. Systemic hormones come up from a variety of glands throughout the torso; the spleen does not take an endocrine office. White blood cells are synthesized in bone marrow and mature in the marrow and thymus. Serum proteins are synthesized in the liver.
Which of these is a lymphoid organ that is active in young children, but decreases in size and importance in machismo?
Possible Answers:
Tonsils
Lymph nodes
Spleen
Thymus
Adenoids
Explanation:
The thymus is a lymphoid organ located in the mediastinal space. The thymus is the site of T-lymphocyte differentiation. The mature T-cells leave the thymus and migrate to the spleen, lymph nodes, and other lymphoid tissues where they control prison cell-mediated immune responses. The thymus grows from birth to puberty, at which indicate it begins to shrink. The reason for this involution may be that the organ has produced plenty T-cells and is no longer necessary.
The spleen is another lymphocyte-producing organ. The spleen filters blood, exposing it to lymphocytes that destroy foreign particles. The size of the spleen remains abiding, except in cases of infections such equally mononucleosis. The tonsils are a patch of lymphoid tissue that contain lymphocytes located in the pharynx. The tonsils and adenoids grade a ring of immunologically agile tissue. These tissues remain at a constant size except when infected by bacteria. Lymph nodes receive lymph from a single organ or region of the body. An increase in size, known as lymphadenopathy, could result from combating infection or cancer.
Which lymphoid organ is the site of erythrocyte, leukocyte, and lymphocyte production?
Possible Answers:
Thymus
Spleen
Lymph nodes
Tonsils
Adenoids
Explanation:
The spleen forms erythrocytes (red blood cells), and leukocytes (white blood cells, including lymphocytes) during the embryonic phase. After birth, only lymphocytes are produced.
The tonsils and adenoids are patches of lymphoid tissue located in the pharynx that filter pathogens that enter the body through the oral cavity and olfactory organ. Lymph nodes produce lymphocytes in response to infections past pathogens. The thymus is an organ that produces lymphocytes in infants and immature children.
The surface of which lymphoid organ is covered with stratified squamous epithelium and located at the entrance to the oropharynx?
Possible Answers:
Thymus
Tonsils
Spleen
Lymph nodes
Adenoids
Explanation:
The surface of each tonsil is covered with stratified squamous epithelium, which forms deep crypts that detect and reply to pathogens entering the body. The tonsils are located on either side of the throat at the back of the tongue.
Adenoids are lymphoid tissue located in the nasopharynx, in the midline at the back of the throat. The spleen is in the upper left quadrant of the belly. The spleen has a smooth surface, every bit it is covered past an outer capsule of connective tissue. The thymus is in the mediastinum between the lungs. The thymus is equanimous of two lobes containing multiple lobules divided into an outer cortex and an inner medulla. The thymus is the site of T-cell differentiation. Lymph nodes filter lymph and remove foreign particles. Lymph nodes are located throughout the body, and are concentrated in the neck, axilla, and groin.
What lymphoid organ is one of the principal sites of cancer metastasis?
Possible Answers:
Lymph nodes
Thymus
Spleen
Adenoids
Tonsils
Correct answer:
Lymph nodes
Explanation:
Lymph nodes function to drain lymph. As lymph carries interstitial fluid, it also carries pathogens and cancer cells. Malignant cells may spread through the lymphatic apportionment.
Tonsils and adenoids are collections of lymphoid tissue in the pharynx that filter microbes that enter through the mouth and nose. They enlarge during infectious processes. The spleen filters blood, exposing it to macrophages and lymphocytes that destroy foreign particles and anile blood cells. The thymus is the primary site for T-cell differentiation. The mature T-cells exit the thymus and travel to the spleen, lymph nodes, and other lymphoid tissue where they command cell-mediated immune responses.
The lymphoid tissues are responsible for creating, storing, and processing lymphocytes, which are essentially the effector cells of the immune system. Which of the post-obit is a lymphoid construction that is also responsible for recycling one-time ruby blood cells?
Possible Answers:
Spleen
Liver
Thymus
Appendix
Bone marrow
Explanation:
The spleen is a lymphoid structure that contains resident lymphocytes that produce antiobodies, besides as T-cells that are released into the bloodstream. It also contains resident macrophages, which are responsible for removing and degrading microbes and worn-out scarlet blood cells.
Destruction of the lymph nodes would most likely touch on the allowed system in which way?
Possible Answers:
Inability to initiate and sustain an inflammatory response at the site of infection
Inability to produce killer T cells
Inability to bind antibodies to an antigen
Inability to carry out a 2nd response to an antigen significantly shorter in duration than the first
Correct respond:
Disability to conduct out a 2nd response to an antigen significantly shorter in duration than the first
Explanation:
The secondary response of the immune system is significantly shorter in elapsing due to the storage of memory cells after the initial infection has been combated. During the chief infection, a B-cell will bind with an antigen. In one case this occurs, the B-cells will begin to divide rapidly into plasma cells and memory cells. Plasma cells release high quantities of antibodies, which are integral in combating the infection. Retentivity cells are stored in lymph nodes so that if the same antigen is always encountered again, information technology can exist quickly dealt with by a fast-responding product of the correct form of plasma jail cell. If lymph nodes were destroyed, memory cells would non exist able to mount this quick secondary response.
All MCAT Biology Resources
Report an consequence with this question
If you lot've constitute an issue with this question, delight let united states of america know. With the aid of the community we tin can continue to amend our educational resources.
DMCA Complaint
If yous believe that content available by means of the Website (equally defined in our Terms of Service) infringes ane or more of your copyrights, please notify us by providing a written notice ("Infringement Notice") containing the information described below to the designated agent listed below. If Varsity Tutors takes action in response to an Infringement Notice, it will make a proficient religion attempt to contact the party that made such content available by means of the nearly recent email accost, if any, provided by such political party to Varsity Tutors.
Your Infringement Discover may be forwarded to the party that made the content available or to third parties such every bit ChillingEffects.org.
Please be brash that you lot will be liable for damages (including costs and attorneys' fees) if you materially misrepresent that a production or activity is infringing your copyrights. Thus, if you are not certain content located on or linked-to by the Website infringes your copyright, yous should consider first contacting an attorney.
Please follow these steps to file a notice:
Y'all must include the post-obit:
A physical or electronic signature of the copyright owner or a person authorized to act on their behalf; An identification of the copyright claimed to have been infringed; A clarification of the nature and exact location of the content that you claim to infringe your copyright, in \ sufficient detail to permit Varsity Tutors to find and positively identify that content; for example we require a link to the specific question (not merely the name of the question) that contains the content and a clarification of which specific portion of the question – an epitome, a link, the text, etc – your complaint refers to; Your name, accost, telephone number and email address; and A argument by you: (a) that you believe in good organized religion that the utilise of the content that you claim to infringe your copyright is not authorized past constabulary, or past the copyright owner or such possessor's amanuensis; (b) that all of the information contained in your Infringement Notice is accurate, and (c) under penalty of perjury, that you are either the copyright owner or a person authorized to human action on their behalf.
Transport your complaint to our designated agent at:
Charles Cohn Varsity Tutors LLC
101 S. Hanley Rd, Suite 300
St. Louis, MO 63105
Or fill out the grade below:
Which Lymphoid Organ Filters Lymph?,
Source: https://www.varsitytutors.com/mcat_biology-help/lymphoid-organs
Posted by: irvinhaster.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Which Lymphoid Organ Filters Lymph?"
Post a Comment